
Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria: How They Work and Best Plants to Host Them
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are nature’s miracle workers, converting atmospheric nitrogen into a form plants can use. The most common searches bring you here, so let’s dive into exactly how Rhizobium, Frankia, and other bacteria perform this essential task, which plants form symbiotic relationships with them, and how you can harness this power in your garden or farm.
Nitrogen is one of the key elements for plant growth and development, recognized as a primary nutrient in agriculture. Maintaining appropriate nitrogen levels in the soil is one of the significant challenges faced by farmers and gardeners. A natural method to supply the nitrogen needed for agriculture is to preserve and fix nitrogen in the soil. In this article, we explain methods to preserve soil nitrogen and introduce nitrogen-fixing plants. By understanding these plants and utilizing them, we can achieve sustainable and healthy agriculture that not only improves soil quality but also contributes to environmental preservation.
What Are Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria? Types and How They Live
There are two types of Nitrogen-fixing bacteria: free-living and symbiotic. In this table, you can see a simple comparison for visual appeal and quick scanning of these types of bacteria.
| Key Function | Host Plant / Lifestyle | Example Genera | Bacterium Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Live in root nodules, fix N for plant in exchange for carbs | Legumes (Beans, Peas, Clover) | Rhizobium, Bradyrhizobium | Symbiotic |
| Live in root nodules of specific woody plants | Non-legumes (Alder, Bayberry) | Frankia | Symbiotic |
| Fix N independently, contribute to soil fertility | Soil, root surfaces | Azotobacter, Azospirillum | Free-Living |
The Importance of Nitrogen in Agriculture and Ecosystems
Nitrogen is a fundamental element for plant growth and development. It acts as a key component in critical compounds such as proteins and enzymes, playing a vital role in plants’ metabolic processes. In agriculture, nitrogen is recognized as one of the most consumed nutrients, alongside phosphorus and potassium. This element helps plants grow, produce more crops, and improve the quality of fruits and vegetables. When leaves have sufficient nitrogen, their photosynthesis rate increases. A nitrogen deficiency causes leaves to turn yellow and fade.
Given the high nitrogen requirements of plants, farmers must use nitrogen fertilizers. But what are nitrogen fertilizers? Nitrogen fertilizers are chemical fertilizers containing nitrogen that help regulate nitrogen levels in the soil. Interestingly, nitrogen is not only important for plants but also for ecosystems. Many living organisms in the soil feed on nitrogen, thereby maintaining biodiversity. A balanced ecosystem enhances the fertility of agricultural lands.

Methods to Increase Soil Nitrogen
To improve soil fertility and increase agricultural yields, nitrogen and other essential nutrients must be made available to plants. Fertilization alone cannot be the solution for increasing plant nitrogen, as excessive fertilization is harmful to both plants and ecosystems. The most important methods for increasing soil nitrogen include:
- Use of Nitrogen Fertilizers (e.g., Barno Ammonium Sulfate): The primary method for increasing soil nitrogen is fertilization with nitrogen-based fertilizers. Ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate fertilizer, and urea are the main fertilizers used to supply nitrogen to plants. Additionally, high-nitrogen NPK fertilizers can also add nitrogen to the soil to some extent.
- Nitrogen-Fixing Plants: Nitrogen-fixing plants, such as legumes (e.g., beans, peas, and lentils) and clovers, have the ability to absorb nitrogen from the air and transfer it to the soil. These plants collaborate with nitrogen-fixing bacteria to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form usable by plants. After harvesting these plants, their roots and residues can help retain nitrogen in the soil.
- Crop Rotation: In crop rotation, agricultural crops are planted periodically in a given field. This method involves alternating crops that consume nitrogen with those that fix nitrogen.
- Organic Fertilizers: Composts and animal manures improve soil quality and increase nutrients like nitrogen.
- Preventing Nitrogen Leaching: Nutrient leaching from the soil is a significant challenge for farmers. One way to preserve soil nitrogen is to prevent nutrient leaching. To achieve this, reducing irrigation, using mulches, improving soil texture, and applying slow-release fertilizers are recommended.
- Balanced Use of Pesticides and Herbicides: Excessive use of chemicals such as pesticides and herbicides destroys beneficial soil bacteria. These bacteria play a role in nitrogen fixation, so their loss reduces nitrogen fixation in the soil.
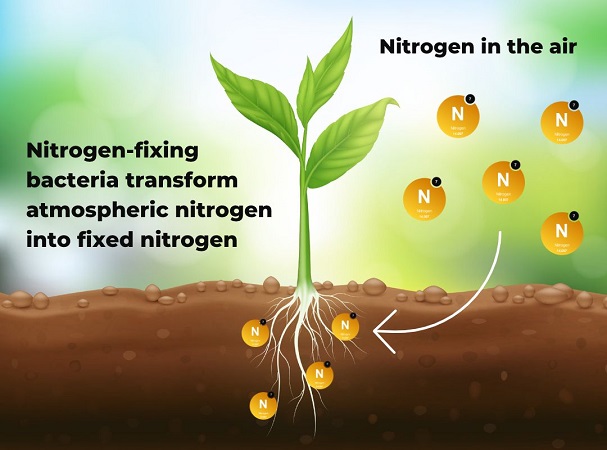
How Does Nitrogen Fixation by Plants Work?
Nitrogen is a critical element in nature, making up 78% of the air’s volume in the form of nitrogen molecules. However, this nitrogen is not directly absorbable by plants. Therefore, molecular nitrogen must first be made usable for plants and then converted into a component of organic compounds. A significant portion of atmospheric nitrogen is converted into ammonia, nitrate, and nitrite by soil bacteria.
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria live in two forms: free-living and symbiotic. Symbiotic bacteria live in a mutualistic relationship with plants. Rhizobium bacteria, for example, are symbiotic with legumes and reside in the root nodules of these plants. Frankia, on the other hand, is symbiotic with non-leguminous plants and lives in their root nodules. Free-living bacteria are not dependent on other organisms and primarily contribute to the carbon cycle. Some strains of these bacteria can also be effective in nitrogen fixation.
The roots of nitrogen-fixing plants, such as peas, contain Rhizobium bacteria. These bacteria capture nitrogen from the air and convert or “fix” it into a form essential for their growth. Once their use of nitrogen is complete, the bacteria make themselves available to the plant. This is an example of a symbiotic relationship between plants and bacteria, and the process is called “nitrogen fixation.”
In simple terms, the nitrogen fixation process involves the following steps:
- Nitrogen Absorption: Rhizobium bacteria absorb gaseous nitrogen from the atmosphere.
- Nitrogen Conversion: These bacteria use specific enzymes to convert nitrogen gas into ammonia.
- Plant Nutrition: The produced ammonia is converted into other compounds, such as nitrate, which are then absorbed by the plant.

Which Plants Are Nitrogen-Fixing?
Nitrogen-fixing plants are divided into two main categories: leguminous and non-leguminous plants. Leguminous plants belong to the Leguminosae family and have unique characteristics in nitrogen fixation. The most important nitrogen-fixing plants include peas, various types of beans, fava beans, split peas, and vetch. Research indicates that plants like aloe vera and bay laurel shrubs can also contribute to nitrogen fixation, but their effectiveness is lower than that of legumes.
Farmers utilize the nitrogen-fixing properties of legumes to enrich the soil. They plant their desired crop one year and then grow legumes or other nitrogen-fixing plants the following year.
Benefits of Using Nitrogen-Fixing Plants
- Increased Soil Fertility: Nitrogen-fixing plants increase soil nitrogen levels by converting gaseous nitrogen into absorbable forms. This improves soil quality and enhances its fertility.
- Reduced Need for Chemical Fertilizers: By naturally fixing nitrogen in the soil, the need for chemical fertilizers decreases. This not only reduces farmers’ costs but also helps preserve the environment and reduce pollution.
- Improved Soil Structure: The roots of nitrogen-fixing plants strengthen soil structure. These roots can soften the soil, allowing better penetration of water and air.
- Biodiversity: Using these plants increases biodiversity in fields. The presence of diverse plants can attract beneficial insects and help control pests.
- Reduced Soil Erosion: Nitrogen-fixing plants, by creating vegetative cover, prevent soil erosion and help retain soil moisture.
- Strengthened Food Chain: By supplying nitrogen, these plants improve the quality of agricultural products, thereby strengthening the food chain.
- Environmental Preservation and Improvement: Reducing the use of chemical fertilizers and improving soil quality help preserve ecosystems and water resources. Additionally, these plants can contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
By adopting nitrogen-fixing plants and sustainable agricultural practices, farmers can enhance soil health, reduce environmental impact, and promote long-term productivity. This approach not only benefits agriculture but also contributes to a healthier planet.
Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria FAQ
Yes, rhizobial inoculants are sold for legumes like peas and beans. For non-legumes, focus on planting the host plants themselves.
They are most effective in well-drained, moderately fertile soils with the right pH (often slightly acidic to neutral). Poor, compacted, or highly acidic soils can limit their activity.
While both are beneficial soil microbes, bacteria fix nitrogen from the air. Mycorrhizal fungi form a network that helps plants absorb water and phosphorus from the soil.
