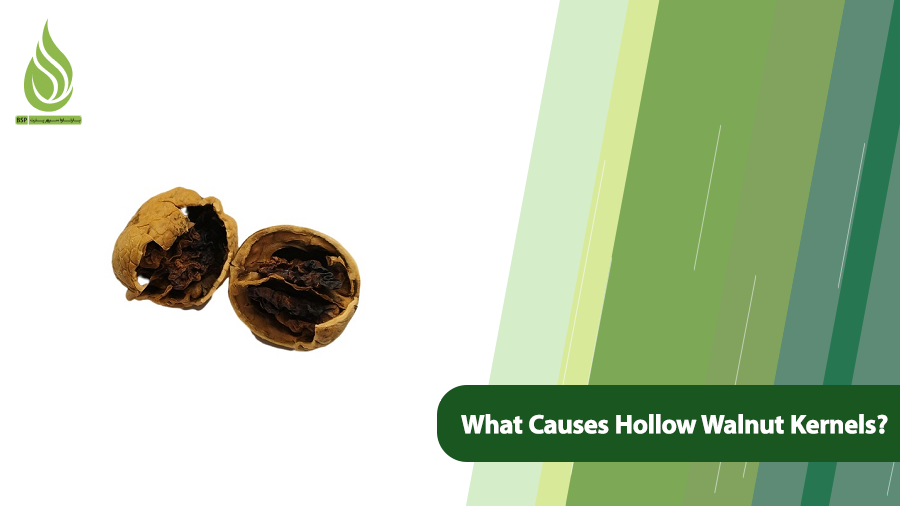
What Causes Hollow Walnut Kernels? How to Prevent This Issue?
Hollow walnut kernels are a common challenge in cultivating this valuable crop. While minor shrinkage may affect only a small percentage of the harvest, there are instances where a significant portion of walnuts end up hollow or discolored. Factors such as nutrient deficiencies, pests, and environmental conditions can all contribute to this problem.
In this article, we explore the causes of hollow walnut kernels and effective strategies to prevent them. Join us as we break down key insights and practical solutions to safeguard your walnut crop.
Understanding Hollow Walnut Kernels
You might crack open a walnut only to find no kernel inside or a low-quality one—even if the shell appears perfectly intact. While a few hollow nuts may seem negligible, a high number of empty kernels signals an underlying issue with the walnut trees, such as nutrient gaps or improper care.
Walnuts are a vital food source in many countries, prized for their protein, vitamins, and healthy fats. Cultivating high-quality walnuts not only boosts agricultural economies but also sustains farmers’ livelihoods. Conversely, hollow kernels directly reduce yields and profits, leading to significant financial losses.
Degrees of Kernel Hollowing
Hollow walnuts vary in severity. Some may have smaller or lower-quality kernels but remain edible, while others are entirely empty. To detect hollowness, the shell must be cracked open. However, buyers can use a simple trick to spot hollow walnuts: Hold a walnut in your palm and shake it gently. A full, healthy kernel will feel solid and heavy, while a hollow one will feel lighter and may rattle.
To combat this issue, farmers must identify and address the root causes.

Causes of Hollow Walnut Kernels
Hollow walnut kernels can occur due to several factors. The most significant causes include:
- Unfavorable Weather Conditions: Fluctuations in temperature, especially sudden frosts during flowering, can damage kernels and reduce their quality. Excessively low or high humidity levels also negatively impact kernel development.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: A lack of essential nutrients like nitrogen, potassium, calcium, and others weakens walnut structure, leading to hollow kernels. Poor soil quality or improper fertilizer use exacerbates this issue.
- Pests and Diseases: Infestations by pests such as walnut husk flies or codling moths, as well as diseases like powdery mildew, can destroy kernel tissue and degrade quality.
- Poor Orchard Management: Improper irrigation, inadequate pruning, and overcrowded tree spacing harm tree health and reduce kernel quality.
- Environmental Stress: Sudden environmental changes, such as drought or overwatering, stress trees and affect kernel development.
- Tree Age: Older trees are more vulnerable to pests and diseases, increasing the likelihood of hollow kernels.
- Walnut Variety: Certain walnut varieties naturally produce lower-quality kernels or are prone to hollowness. When purchasing saplings, ensure the variety is high-quality and suited to your local climate.
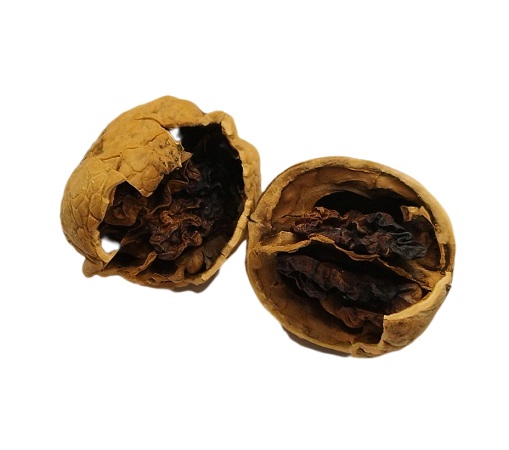

Preventing Hollow Walnut Kernels: Effective Strategies
Based on the root causes discussed earlier, here are actionable solutions to minimize hollow kernels and ensure a healthy walnut harvest:
Select Resilient Walnut Varieties
Some walnut varieties are naturally prone to hollowness. When purchasing saplings, choose varieties proven to thrive in your local climate and soil conditions. Opt for disease- and pest-resistant cultivars to reduce the risk of hollow kernels.
Ensure Proper Tree Spacing and Pruning
- Adequate Spacing: Maintain proper distance between trees to improve airflow, reduce competition for resources, and enhance kernel quality.
- Strategic Pruning: Regularly prune mature trees to remove excess branches. This boosts air circulation, allows sunlight to penetrate the canopy, and directs the tree’s energy toward fruit development. Proper pruning also ensures nutrients are distributed efficiently, leading to denser, healthier kernels.
Optimize Irrigation Practices
Avoid both underwatering and overwatering, which stress trees and harm kernel development. Implement a drip irrigation system to deliver consistent moisture, especially during critical growth phases (flowering, nut formation, and kernel filling).
Protect Trees from Frost Damage
Walnuts thrive in cool climates but are vulnerable to extreme cold. Late spring frosts can damage flowers, while harsh winters may weaken trees. Mitigate risks by:
- Using frost blankets or windbreaks during cold snaps.
- Lighting controlled fires (smudge pots) in orchards to raise temperatures on freezing nights.
Manage Pests and Diseases Proactively
- Biological Controls: Adopt sustainable practices like introducing natural predators (e.g., ladybugs for aphids) or using pheromone traps.
- Chemical Solutions: Apply targeted pesticides or fungicides only when infestations occur. Focus on threats like walnut husk flies, codling moths, and powdery mildew.
- Regular Inspections: Monitor trees for early signs of pests, diseases, or nutrient deficiencies. Act swiftly to treat issues before they escalate.
Maintain Soil Health and Nutrition
Test soil regularly and address deficiencies in nitrogen, potassium, calcium, and boron—key nutrients for kernel development. Use organic compost or balanced fertilizers to enrich poor soils.
Preventing hollow walnut kernels requires a holistic approach: choosing resilient varieties, optimizing orchard conditions, and addressing stressors like pests, frost, and poor nutrition. By combining these strategies, growers can improve kernel quality, maximize yields, and ensure long-term orchard health.
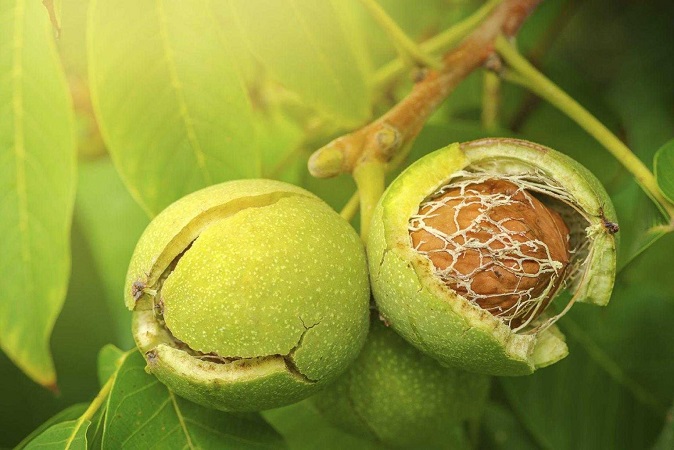

The Importance of Proper Nutrition for Plump Walnut Kernels
For walnut trees to thrive and produce high-quality, plump kernels, they require balanced nutrition. Walnut trees, like all plants, depend on a mix of macro- and micronutrients, all of which must be available in adequate quantities to support optimal growth. Among these, nitrogen (N), potassium (K), and phosphorus (P) are the most critical macronutrients, forming the backbone of a tree’s nutritional needs. These are found in NPK fertilizer, which is one of the most used fertilizers.
Fertilization: The Key to Nutrient Supply
Nutrients are primarily delivered through fertilization. However, fertilizers must be applied in precise amounts tailored to the tree’s requirements. Both over-fertilization and under-fertilization can harm tree health and reduce kernel quality. To determine the exact needs of your trees:
- Conduct annual soil tests before the growing season.
- Use test results to adjust soil conditions and create a customized fertilization plan that addresses deficiencies.
We suggest you take a look at our guide to walnut tree fertilization.
Nutrient Deficiencies and Their Impact
While all nutrients matter, shortages of specific elements disproportionately affect kernel development:
- Iron (Fe): Essential for chlorophyll production; deficiency weakens trees.
- Potassium (K): Critical for water regulation and sugar transport; low levels lead to shriveled kernels.
- Boron (B): Vital for cell wall formation and pollination; deficiency causes hollow or misshapen kernels.
- Zinc (Zn): Supports enzyme function; shortages stunt growth and reduce yields.
Additionally, timely applications of nitrogen-rich fertilizers (to boost foliage) and calcium-based products (to strengthen cell structure) are crucial during specific growth stages.
Balanced Fertilization = Plump Kernels
As highlighted in our previous article on Walnut Tree Fertilization, a science-backed approach to nutrient management is non-negotiable. Addressing deficiencies through targeted fertilization not only enhances kernel density but also improves disease resistance and overall tree vigor.
Key Takeaway:
Regular soil testing, combined with a balanced macro- and micronutrient program, ensures walnut trees receive the “diet” they need to produce plump, marketable kernels. Skip the guesswork—let soil science guide your fertilization strategy!

Consult the Experts
To accurately diagnose the causes of hollow walnut kernels, seek guidance from agricultural specialists or experienced local growers. These experts can leverage their knowledge and hands-on experience to identify underlying issues and recommend targeted solutions to revitalize your walnut trees. Consulting professionals also empowers farmers to adopt modern techniques and improved management practices, enhancing crop quality and preventing future problems.