
The basics of seedling planting and important things you should know
Systematically planting seedlings is a critical process that plays a pivotal role in maintaining the sustainability of gardens and trees. Ensuring that seedlings are planted and tended to in a standardized fashion sets the stage for healthier trees in the future, maximizing their productivity. Neglecting the proper management of the seedling planting process can result in compromised tree growth down the line and subpar tree yields.
In this piece, we aim to elucidate the steps for planting seedlings correctly and delve into the optimal timing for planting various types of seedlings. Additionally, we will underscore key considerations for planting different seedlings.
Why is it crucial to plant seedlings properly?
The right planting approach involves choosing robust seedlings, prepping the planting site effectively, planting at the correct depth and spacing, and providing post-planting care. Notably, a significant share of the issues seen in orchards stems from haphazard seedling planting practices. Here’s why planting seedlings properly holds significant importance:
- Tree Growth and Longevity: When seedlings are planted and nurtured correctly, the chances of robust tree growth and long-term survival are heightened.
- Extended Tree Lifespan: Trees planted using principled methods typically enjoy a longer lifespan due to their well-established root systems and sound initial structures.
- Enhanced Tree Performance: Properly planted trees generally exhibit improved growth, yield more fruit, and boast denser foliage due to meeting the tree’s growth needs right from the start.
- Resource Conservation: Adhering to correct planting techniques promotes more efficient use of resources like water, fertilizers, and energy, curbing resource wastage. We suggest you take a look at fruit trees fertilizer too.
- Biodiversity Preservation: Proper tree planting practices aid in preserving natural habitats and biodiversity.
Improper tree planting can lead to a host of issues including root stunting, diminished water and nutrient uptake, root decay, sensitivity to extreme temperatures, vulnerability to drought, and reduced overall yield, highlighting the significant drawbacks of careless tree planting practices.
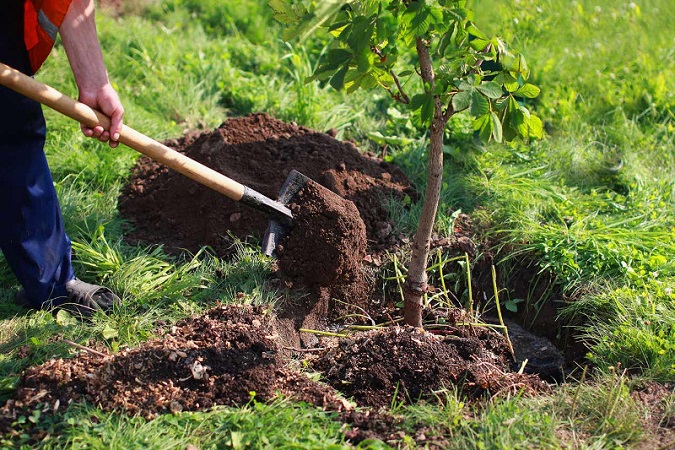

Key Factors in Seedling Planting
To ensure proper seedling planting, it is crucial to prioritize these factors:
- Taking into account environmental conditions and selecting appropriate seedlings for planting
- Soil cultivation and land plowing
- Soil fertilization
- Considering the optimal timing for seedling planting
- Attention to planting techniques
- Post-planting care
Considering Environmental Conditions and Selecting Appropriate Seedlings for Planting
The choice of tree species and the timing of planting seedlings are greatly influenced by the planting site and the local climate conditions. The weather patterns of a region play a crucial role in the growth and sustainability of its trees. Some trees thrive in warm climates, while others flourish in mountainous terrains.
Seedlings must be well-suited to factors such as the degree of cold on the coldest days of the year, heat levels on the hottest days, sunlight exposure throughout the day, moisture levels in the area, annual precipitation, and more. The selection of the right seedlings also hinges on considerations like soil type, available space, and the preferences and expertise of the gardener.
Several factors should be taken into account when choosing suitable seedlings:
- Compatibility of the seedling with the region’s climate
- The health of the seedling in terms of pests and various diseases: This involves inspecting the health of the seedling’s stem, leaves, and roots.
- Method of seedling cultivation: Seedlings are propagated through grafting, seeding, vegetative propagation, modified techniques, and other processes, each with its unique traits. Paying attention to the propagation method when selecting a seedling is crucial. Generally, grafted and modified seedlings tend to be more compact, adaptable, and productive.
- Seedling age: A two-year-old seedling is typically the optimal age for planting. At this stage, the seedling has achieved sufficient growth and is better suited to the environmental conditions.

Soil Preparation and Plowing Operations
Before planting seedlings, it is essential to conduct soil preparation, also known as tillage, on the agricultural land. During soil preparation, the land is leveled, and soil testing is performed. Soil testing provides detailed information about soil texture, drainage, permeability, soil salinity, and the soil nutrients present.
The ideal soil for planting seedlings is loamy, free from salinity, lime, and gypsum, with proper drainage, and rich in soil nutrients. In such soil, seedling roots can thrive and develop abundant lateral and surface roots. After soil testing and understanding the soil requirements, debris and weeds are cleared from the land. Ultimately, the land needs to be plowed.
Before plowing, if the soil is excessively dry, it is irrigated. Subsequently, the plowing operation is carried out.
Plowing the soil makes it more pliable, creating a favorable environment for seedling root growth. It reduces soil compaction, providing an improved growth environment. Plowing facilitates the transfer of surface nutrients to deeper soil layers. Additionally, fertilization ensures that nutrients penetrate the soil easily, making them accessible to the roots.
Soil Fertilization
Soil testing is crucial in determining the soil’s nutrient requirements, allowing us to take necessary steps to address any deficiencies or overabundance of nutrients. Depending on these needs, soil requires fertilization. Soil corrective fertilizers are typically applied to the land after plowing and before the planting season commences. Organic fertilization is usually carried out before the planting season using materials like animal manure and compost, which slowly release nutrients into the soil over time.
Generally, mineral fertilizers are not utilized for fertilization before planting seedlings. These fertilizers break down rapidly and become accessible to plants. Since no seedlings have been planted at the fertilization stage, mineral fertilizers do not offer significant benefits. Various fertilizers are available to promote seedling growth, root development, and leaf production. For instance, ammonium sulfate crystals are rich in nitrogen and sulfur. However, using this fertilizer before planting seedlings or even in the early stages after planting is not advisable. To maximize the benefits of chemical fertilizers, understanding the appropriate timing for each type is essential. If you lack experience in this area, consulting with an agricultural expert is strongly recommended.
Considering the Timing of Seedling Planting
Paying attention to when you plant your seedlings is vital. The timing of seedling planting is directly influenced by the climate of each region. Planting seedlings is typically carried out in early winter (early spring) and early fall, taking into consideration the climate conditions and tree characteristics. In colder regions, seedling planting usually occurs after the frost season ends. However, in tropical and temperate regions, seedling planting is commonly postponed to early fall.
Let’s take a look at the best times to plant several fruit trees:
- Walnut tree: Early spring
- Almond tree: Mid-November to early December
- Grapevine seedling: Late winter and early spring
- Pistachio seedling: Late winter and early spring
- Peach seedling: Mid-winter
- Cherry seedling: Mid-winter
- Apple seedling: Spring
- Apricot seedling: Early spring
- Plum: Early summer
These are approximate and widely accepted planting times for seedlings. For specific planting guidance tailored to your location, it’s advisable to consult with an agricultural expert or an experienced farmer.
Attention to Planting Techniques
The method of planting each tree varies based on its characteristics. Trees not only have different environmental requirements and planting times, but they also differ in planting depth, spacing, and root systems.
When planting seedlings, the first step is to determine the spacing and planting pattern. This distance is determined by considering the volume and height of the trees at maturity. For example, for walnut trees, a spacing of 6×6 feet is considered. In most fruit trees, a spacing of 4×4 feet is used, while for smaller trees like cherries, a distance of 3×3 feet is typical.
After establishing the planting pattern, it’s time to dig the planting holes. These holes can be dug either at the time of planting the seedlings or a few weeks before. The depth and width of the holes are determined by the size of the roots and soil structure. The ideal depth for planting a seedling is between 70 to 100 centimeters.
Now, it’s time to place the seedling in the hole. It’s advisable to disinfect the roots before planting. Before planting, carefully inspect the roots of the seedling, trimming any dried, blackened, or decayed parts with pruning shears. Following this step, use root disinfectant solutions to sterilize the roots before planting.
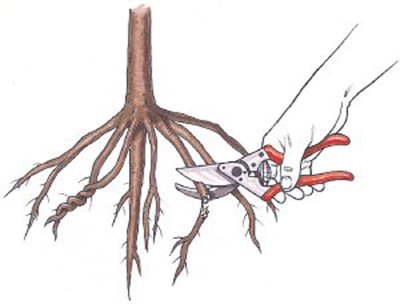
ensure that the seedling’s roots do not get tangled within the hole
To plant a seedling, begin by adding some animal manure into the hole and positioning the seedling vertically inside it. Ensure that the seedling’s roots do not get tangled within the hole. To prevent this, you can create a small mound of soil in the hole and arrange the roots around it in a radial fashion. The seedling’s collar should be positioned 10 centimeters above the soil surface. Once the seedling is placed in the center of the hole, fill the surrounding area with soil and compact the soil around the collar using a shovel.
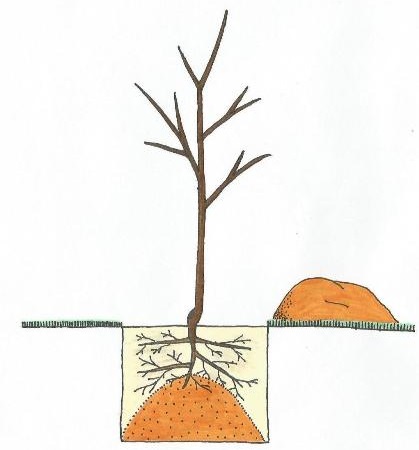
To prevent seedling damage or tipping over in windy conditions, consider using stakes during planting. Pay close attention to how the roots are positioned in the hole. Proper root placement enhances nutrient uptake and absorption.
An essential consideration regarding root depth is that nutrients are typically found within 10-15 centimeters of the soil surface. Surface soil, with its increased oxygen and microbial activity, provides a richer nutrient environment. Surface roots, closer to the ground, are responsible for absorbing nutrients, while deeper roots primarily absorb water. Therefore, for optimal access to soil nutrients and conducive growth conditions, avoid planting the seedlings too deeply.
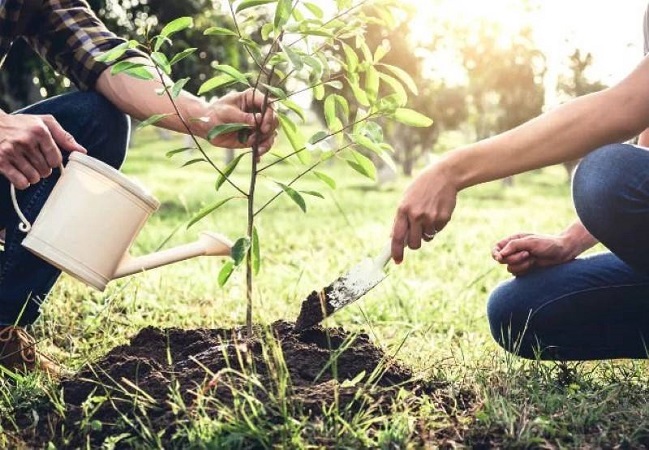
Post-Planting Care for Seedlings
After planting a seedling, it’s essential to promptly water it to ensure root moisture and proper establishment. If possible, erect protective barriers around the seedlings to ward off animals. Pruning newly planted seedlings is a critical task as it stimulates new leaf and branch growth. Additionally, pruning fosters proper framework development and enhances future tree productivity. After pruning, seal the pruning cuts with pruning sealant to prevent pest infestation.
Fertilizing the seedlings after planting is another vital aspect of care. Fertilization promotes robust seedling growth. However, applying fertilizer immediately after planting is not recommended. The type and timing of fertilization are determined by an agricultural specialist based on the seedling’s age, condition, and soil deficiencies. The specialist identifies the necessary fertilizers and schedules the fertilization accordingly.
Key Considerations for Seedling Planting
- Ensure you procure seedlings from reputable nurseries as the quality of the seedling significantly impacts its growth and future tree productivity.
- The shorter the interval between acquiring and planting the seedlings, the better.
- Handle the transportation of seedlings with care to prevent any damage during transit.
- Avoid exposing the seedling roots to air until planting time.
- Verify that the roots, stem, and branches of the seedling are in good health and natural condition.
- Trim any damaged roots before planting to minimize the risk of pests and diseases.
- Disinfecting the roots before planting aids in maintaining their health. A blend of loamy soil, organic fertilizer, fungicide, and ash is typically used for this purpose. Soak the roots in this mixture before placing them in the planting hole.
- Ensure the planting hole has a maximum diameter of 100 centimeters and a depth of up to 100 centimeters for optimal seedling placement.
- When planting, mix topsoil with manure and pour it near the roots (at the bottom of the hole). Cover the soil surface with the remaining soil.
- Position the seedling in the hole so that the root collar sits above ground level.
- Fill the hole around the roots with soil and press it down to eliminate air pockets around the roots.
- Immediately after planting, water the seedlings.
- In windy regions, secure the seedlings with stakes.
- Opt for drip irrigation as the most effective method for watering seedlings.