What are the stages of preparing agricultural land for cultivation?
Agriculture involves more than just three stages – planting, cultivation, and harvesting. Soil preparation is also a crucial stage that farmers focus on. Land preparation occurs before seed planting. This process involves several stages where soil deficiencies are addressed and the soil is prepared for seed planting. If you want to learn about the steps of preparing agricultural land, stay with us in the following article.
Why is preparing agricultural land important?
Agriculture involves more than simply tilling the land and planting seeds. Without proper land preparation, we cannot expect high productivity from our crops. Land preparation in agriculture is carried out before planting the seeds. At this stage, farmers work to bring the soil to an ideal state to ensure optimal crop productivity in the future.
In agriculture, the activities conducted before planting seeds are known as soil preparation. This involves making the planting bed ready and preparing the land for seed planting. Next, we will explain the stages of agricultural land preparation.
What are the steps of preparing agricultural land?
In summary, agricultural land preparation involves the following stages:
- Soil Testing
- Plowing and Harrowing
- Land Leveling
- Soil Fertilization
- Ridging
- Seed Planting
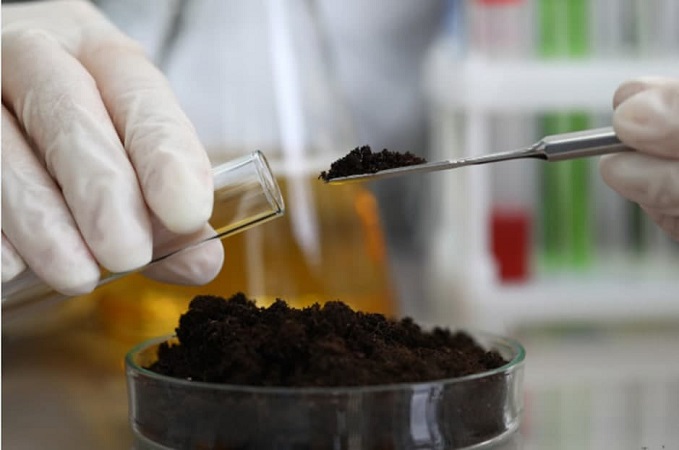
Soil Testing
If you plan to grow crops on agricultural land in the next year, it’s important to check if the soil is suitable for the specific crop. This is done through soil sampling and testing, which involves checking the soil’s pH. Understanding the soil’s pH is crucial to determine which crops can thrive in the soil. Knowing the soil’s pH also allows for adjustments to be made if needed. Regulating the soil’s pH is essential for maintaining high fertility in farms.
Conducting soil testing helps determine if your land has enough nutrients for plant growth. This allows you to pinpoint which nutrients are deficient and address the issue through fertilization. Overall, soil testing provides valuable insights into the soil’s structure and its potential for supporting plant growth.
For soil testing, samples are collected from various parts of the land and analyzed in a soil laboratory.

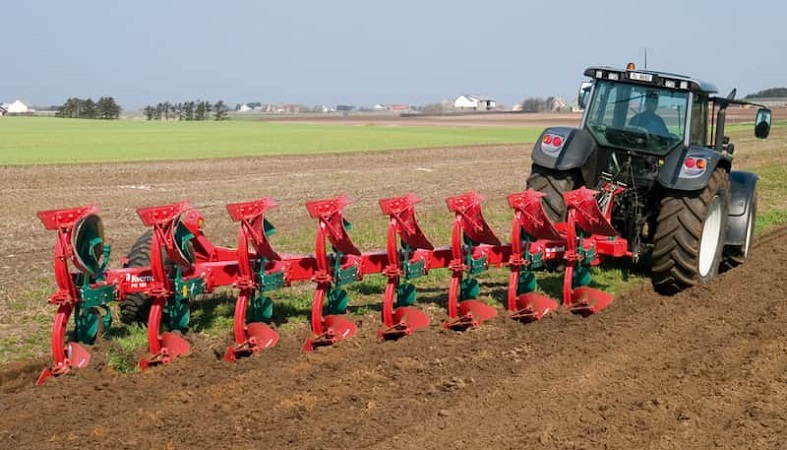
Plowing and Harrowing
One of the crucial stages in agriculture is the process of plowing the land. Plowing the soil creates an optimal bed for plant growth. This process offers several key advantages:
- Plowing provides a suitable ground for rapid water infiltration.
- It allows air to penetrate the soil.
- Creates favorable conditions for root penetration into the soil.
- Eliminates the growth of weeds.
- Organic plant residues are buried under the soil, acting as a form of organic fertilizer.
- Prevents soil erosion.
- Distributes beneficial soil bacteria throughout different areas of the land.
- Separates clods from each other.
- Helps eradicate soil pests and diseases present in the subsoil, preventing damage to future plants.
Plowing is typically carried out using a simple or reversible plow pulled by a draft animal like an ox. Other machinery such as chisel plows, subsoilers, and rotary plows are also used for plowing. Some farmers use a PTO-driven plow for plowing small fields.
The depth of plowing and soil inversion with an ox plow is significant. In this method, the land is plowed to a depth of about 60 centimeters, effectively turning the soil over and breaking up clods. Sometimes secondary tillage is necessary after plowing. In secondary tillage, large soil clumps are broken down into smaller particles, creating a uniform soil texture that is an ideal bed for seed planting.

Weeds significantly hinder the productivity of fields. Plowing the land to some extent eliminates the bed of weeds. Some farmers, to eradicate weeds effectively, irrigate the land before plowing. This allows the weeds to grow, making them easier to uproot during the plowing process. If the land is heavily infested with weeds, herbicides should be used.
Land Leveling
Typically, when preparing land for agriculture for the first time, it needs to be leveled. The irregularities in agricultural land surfaces are referred to as “ridges.” These ridges can complicate agricultural operations at various stages, so it is necessary to level the land before planting seeds.
In small plots with limited ridges, ridges are removed using tools like a hoe and a pickaxe. In larger fields, ridges are eliminated using machinery such as graders, bulldozers, scrapers, and loaders. Land that has not been cultivated before often contains many stones. Large stones must be completely collected from the land’s surface; otherwise, they can cause significant problems during planting and harvesting
In agricultural lands cultivated annually, ridges are not usually extensive. In these lands, the creation of furrows, irrigation channels, human and animal traffic, and tractor passage leads to the formation of ridges. Typically, these ridges are removed through plowing and leveling using a hoe. However, if the agricultural land is extensive, it is better to use machinery to reduce the labor and effort of the farmer.
Preparing Agricultural Land with Soil Fertilization
Plants require nutrient-rich soil abundant in both macro and micronutrients for growth; hence, soil fertilization is necessary. Fertilizing the soil based on its needs enhances soil quality and consequently improves crop quality.
Plowing the land has numerous advantages, as we have highlighted the most important ones; however, it causes the soil to lose its resistance to rainfall and wind. The lack of nutrients and water-soluble nutrients in the soil leads to soil erosion. Therefore, soil fertilization is essential for agricultural lands.
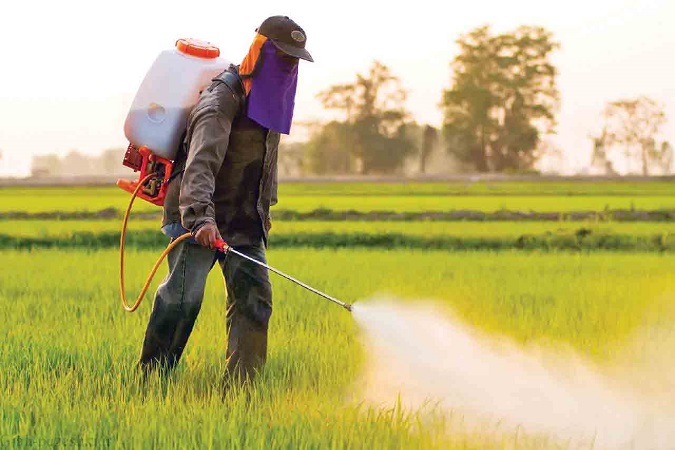

Fertilizing agricultural land is not a once-a-year task. Depending on the land’s needs and the type of crop, fertilization needs to be carried out several times during different seasons. In the stage of preparing agricultural land, organic fertilizers such as plant compost and animal manure are applied to the soil. Sometimes, based on requirements, fertilizer applicators are used to apply various types of chemical fertilizers like nitrogen fertilizers, potassium sulfate, superphosphate, and so on to the soil.
When we plow the soil and add nutrients during the stage of preparing agricultural land, the microscopic organisms in the soil become more active and decompose organic matter. This ensures that in the future, nutrients are available to plants.
Another goal of fertilization is to alter the soil’s pH. In soil tests, soil pH, humus content, nitrogen levels, phosphorus, potassium, and other soil elements are examined. If the soil pH is higher or lower than the standard level, pH correction is performed. If the soil is acidic, lime is added, and if it is alkaline, sulfur is applied to the soil.
Creating Furrows and Ridge Planting
Creating furrows on the soil or ridge planting (planting on mounds) is part of the stages of preparing agricultural land. Plants like corn, sunflowers, cucumbers, etc., are sown on ridges; therefore, before seeding, furrowing and ridge planting need to be carried out. Ridges are created at specific intervals from each other. The spacing of the ridges is determined based on the type of crop. Seed planting is done on both sides of the ridge.
Seed Planting After Preparing Agricultural Land
All the stages we have described are essential for preparing agricultural land. After completing these stages, it is time for seed planting. The farmer, at a specific time, using a seed drill or traditional methods, places the seeds into the soil. The timing and depth of seed planting depend on the type of plant. Some seeds are planted deep in the soil, while others are planted closer to the surface.