
What is NPK fertilizer? When is it used?
One of the most widely used agricultural fertilizers is NPK fertilizer, which is composed of three essential plant nutrients: nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. NPK is beneficial for the nutrition of most plants and trees and is among the most commonly consumed chemical fertilizers. In this article, we will explain the properties of NPK fertilizer and how to use it effectively.
What is NPK Fertilizer?
Plants need nutrients to grow. Without nutrients, plants and trees cannot survive or may not grow as needed. As mentioned, the most consumed and essential nutrients for plants are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). These elements naturally exist in the soil. However, due to excessive cultivation and other environmental factors, the soil faces a shortage of essential elements. Therefore, nutrients need to be applied to the soil or plants in the form of fertilizer. NPK is an abbreviation for these three elements:
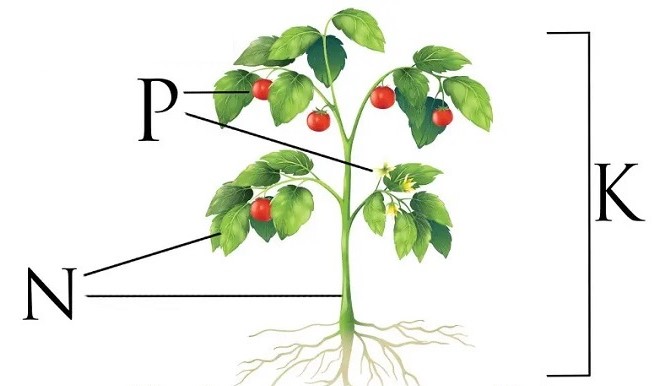
- N: Nitrogen
- P: Phosphorus
- K: Potassium
These elements are among the major nutrients required by plants and fulfill most of the plant’s nutritional needs. For this reason, many people refer to NPK as a complete fertilizer.

NPK fertilizer is offered in two types: balanced and unbalanced:
- Balanced NPK: This term is used when the percentage by weight of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in the fertilizer is the same. For example, NPK 20-20-20 is considered a balanced complete fertilizer.
- Unbalanced NPK: In this type of fertilizer, the levels of nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus are not the same. This fertilizer is used when one element is already present in sufficient amounts in the soil, so the proportion of that element in the NPK mixture is lower. Alternatively, if a certain element is lacking in the plant, a higher percentage of it is included in the NPK mix.
Since this fertilizer is available in various ratios, it is suitable for a wide range of plants, including citrus fruits, trees such as walnut and pistachio, houseplants, etc. Also it’s one of the best walnut trees fertilizers.
The role of each element present in NPK fertilizer
To examine the benefits of NPK fertilizer, let’s take a look at the advantages of each of these elements separately.
The Role of Nitrogen in NPK
The letter N in NPK stands for nitrogen. Nitrogen is responsible for the health of leaves, stems, and branches. This element promotes the production of chlorophyll, giving leaves a vibrant green color. Without nitrogen, plants become discolored and yellow. Additionally, plant growth is stunted without nitrogen. A very good source of nitrogen is ammonium sulfate.
If you are growing vegetables, fruit trees, or plants where leaf quality is important, it’s important to provide the plant with the right amount of nitrogen. If there’s an excess of nitrogen, the plant will prioritize leaf growth over fruit production. This fertilizer is one of the best fruit tree fertilizers.
The Role of Phosphorus in NPK
The letter “P” in NPK represents phosphorus. Phosphorus plays a significant role in root growth and fruiting. This element also plays a crucial role in flower formation in plants and flowering in trees. Phosphorus deficiency leads to weak roots and decreased flower and fruit production. Additionally, phosphorus increases the resilience of plants against environmental stresses such as cold. Providing the necessary phosphorus allows the plant to have better photosynthesis and utilize sunlight effectively.
The Role of Potassium in NPK
The letter K in NPK stands for potassium. Potassium is a crucial nutrient that promotes overall plant growth. It helps plants become more resistant to cold, dryness, pests, and diseases, ultimately improving the overall quality and yield of the plant. Potassium also facilitates the movement of nutrients within the plant during cold and dry seasons, ensuring that the plant remains well-nourished.
Other Constituents of NPK Fertilizer
The primary nutrients in NPK fertilizer (nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus) make up a percentage of the fertilizer’s weight. The remaining weight of the fertilizer is composed of additional substances. These additional substances include calcium, magnesium, iron, and micronutrients to meet the plant’s needs to the fullest extent possible.
When you examine the packaging of NPK fertilizers, you will notice three two-digit numbers on the package. These numbers indicate the percentage by weight of each nutrient. The first number signifies nitrogen, the second number represents phosphorus, and the third number stands for potassium. For example, a fertilizer labeled 10-10-10 means it contains 10% nitrogen, 10% phosphorus, and 10% potassium. The higher these numbers are, the higher the concentration of nutrients in the fertilizer.
In addition to NPK 10-10-10, there are several common types of NPK fertilizers:
- 10-8-10
- 5-10-5
- 20-30-10
- 22-6-20
- 20-20-20
- 5-50-5
- 10-52-10
- 36-12-12
- 40-10-10
How to choose the right complete fertilizer?
The composition of NPK fertilizers varies significantly, depending on the specific needs of the plants and the deficiencies in the soil. It is important to determine the precise NPK fertilizer formula based on the type of plant and the soil’s requirements. To better understand the soil’s needs, it is advisable to take soil samples from the agricultural land and have them tested in a laboratory. This will help in accurately assessing the soil’s requirements and applying NPK or other chemical fertilizers, such as nitrogen fertilizers, as needed.
If you choose the wrong fertilizer or if the soil pH is not adjusted, the plant won’t be able to get the nutrients it needs. Additionally, too much of any of these elements can be harmful to the plant, causing toxicity. Excessive amounts of N-P-K elements can seep into surface and groundwater, harming the environment, human health, and animals. An abundance of these elements can even stop plants from flowering or fruiting.
Therefore, it is crucial to ensure the plant’s needs before fertilizing. Consultation with an agricultural expert and soil testing is necessary to determine the plant’s requirements.

The Best Time for NPK Fertilization
The best season for using NPK fertilizers is spring when plants have a crucial need for nitrogen. Additionally, for greening, flowering, and staying strong, plants require a significant amount of complete fertilizer. However, depending on the soil’s needs, fertilization can also be done in summer or other seasons. Fertilization with NPK is much more limited during fall and winter due to plant dormancy. The optimal time for fertilizing plants is when direct sunlight is not present. Early morning until 8 a.m. and evenings are the best times for fertilizing plants.
How is NPK Fertilization Conducted?
NPK is available in liquid and powder forms. Fertilization with NPK can be done through irrigation, foliar spraying, and fertigation. Fertigation is the most important method, as the fertilizer easily dissolves in water, allowing NPK to enter the soil during irrigation and provide the necessary resources to the plant gradually. In foliar spraying, the fertilizer is applied to the plant using a sprayer.
Fertilizing with NPK can also be done through fertigation. In this method, the absorption rate is slower, allowing the plant to access resources more gradually. hope this helped you. good luck!
